Comparison of DCPP's SGI to Helms Pumped Storage
DCPP is the greatest contributor to California in-state Synchronous Grid Inertia (SGI)
This is the first installment of Californians for Green Nuclear Power’s (CGNP’s) multipart series examining the relative contributions of Diablo Canyon Power Plant (DCPP) and Helms Pumped Storage. The DCPP overview below was taken from a talk I presented on March 20, 2025 to the SLO Retired and Active Men (RAM.)
DCPP Overview
This is a still from a PG&E YouTube Video. This is a photograph of the DCPP power deck (the brown structure) taken from a helicopter. The power deck is about five stories tall. The twin reinforced concrete containments are behind the power deck.
This is the interior view from a PG&E video showing the south end of the DCPP turbine deck. All unit 2 components are painted powder blue to distinguish them from unit 1, whose components are orange. The generator, which is the unit behind the exciter with the pipes near the floor stands about 20 feet tall.
Here’s a close-up of two workers examining a component in the DCPP unit 2 generator to give a sense of scale. Photo credit: PG&E and the Diablo Canyon Independent Safety Committee.
Here’s a DCPP overhead drawing. This was a figure shown on page 102 of 102 from a 2016 NRC FSAR Update. Each half of the turbine building is 371 feet long. The rotating mass of each DCPP steam turbine assembly and generator rotor is roughly 1 million pounds (or 50 tons.) Each generator spins at 1,800 RPM, or five times the rotation speed of the Helms Pumped Storage generator.
Diablo Canyon Power Plant Units 1 and 2 Final Safety Analysis Report (FSAR) Update, Revision 23, December 2016, Docket No. 50-275 Docket No. 50-323 U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission.
https://www.nrc.gov/docs/ML1720/ML17206A048.pdf
Helms Overview
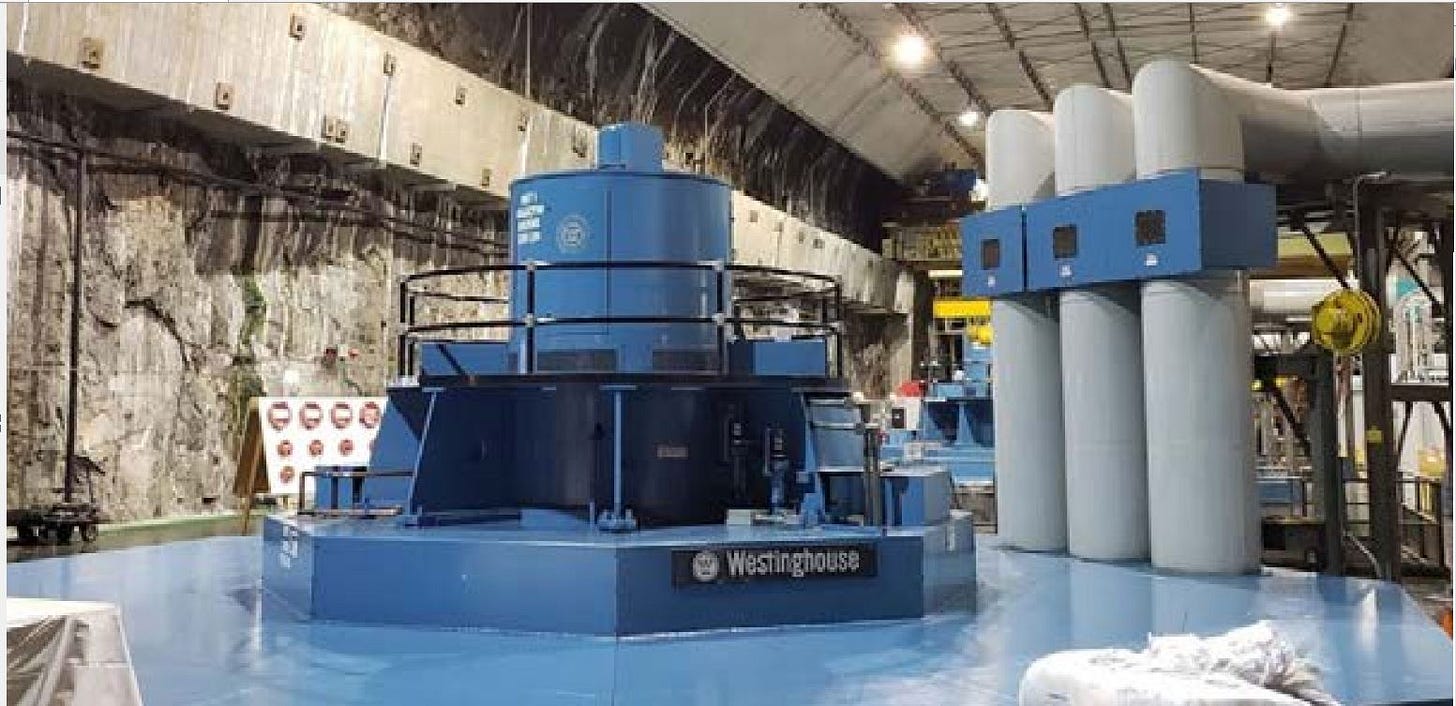
This is a close-up of the top of one of the three pump-generator units at Helms Pumped Storage. The three units at Helms Pumped Storage can generate a combined 1,212 megawatts.
October 10, 2019 Photo Credit the U.S. Department of Energy https://www.energy.gov/sites/prod/files/2019/12/f69/05_ORNL_Signore_HydropowerFleetIntelligence.pdf
Here’s a close-up of two of three of Helms Pumped Storage rotors. Each rotor weighs about 1 million pounds (50 tons.) Each rotor spins at 360 RPM. Each rotor stands about ten feet tall with a outer diameter of about 20 feet. Photo courtesy of Renewable Energy World.
Here’s an overhead view of one of the three Helms Pumped Storage stators. The hole in the middle has an inside diameter of about 20 feet to accommodate the above rotor. Photo courtesy of Renewable Energy World.
With this background information, we can calculate the approximate ratio of the SGI contribution of each DCPP generator to the SGI of each HPS generator.
Relative Contribution to California SGI
Synchronous Grid Inertia Contributions of DCPP and Helms Generators
The formula for synchronous grid inertia (SGI,) often represented by the inertia constant "H", is: H = (J * ω^2) / (2 * S_base),
where J is the moment of inertia of the rotating mass, ω is the rated angular velocity, and S_base is the rated apparent power of the synchronous generator in MVA.
Key points about the formula:
· Meaning of H: This formula essentially calculates the ratio of the kinetic energy stored in the rotating rotor of a synchronous generator to its rated power, giving a measure of the system's ability to resist frequency changes. This is the rotational kinetic energy analog of the linear kinetic energy formula EKE = 1/2 mv2 where m is the mass and v is the velocity.
· Units: H is typically expressed in seconds (s) on a per MVA basis.
· Calculating total system inertia: To calculate the total inertia of a power system, you would sum up the individual inertia constants (H) of all the synchronous generators connected to the grid, taking into account their respective power ratings.
Summary for A2312014: Diablo Canyon Power Plant (DCPP) operates at a speed of 1800 revolutions per minute (RPM.) Helms Pumped Storage operates at 360 RPM S_base is 1,300 MVA for each of the pair of DCPP generators. S_base is 390 MVA for each of the three Helms generators.
Comparison of a DCPP generator to a Helms generator:
For a first order approximation, assume J, the moment of inertia is identical for the DCPP and Helms generator units. k is a proportionality constant which is identical for both generators, Thus, it drops out in the comparison.
HDCPP = k * 1800*1800/2*1300 = k * 1,246
HHelms = k * 360*360/2*390 = k * 166
Thus each DCPP generator produces about 1,246/166 or about 7.5 times the SGI of a Helms generator.
REFERENCES
· Inertia: Basic Concepts and Impacts on the ERCOT Grid
Apr 4, 2018 — Inertia: Basic Concepts and Impacts on the ERCOT Grid. ERCOT Public. 5. For any hour, synchronous inertial response....
https://www.ercot.com/files/docs/2018/04/04/Inertia_Basic_Concepts_Impacts_On_ERCOT_v0.pdf
· "Inertia Estimation of Synchronous Devices: Review of Available Techniques and Comparative Assessment of Conventional Measurement-Based Approaches,"
by Stelios C. Dimoulias, Eleftherios O. Kontis, and Grigoris K. Papagiannis*
Power Systems Laboratory, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, GR-54124 Thessaloniki, Greece
Energies 2022, 15(20), 7767; https://doi.org/10.3390/en15207767
Submission received: 29 September 2022 / Revised: 14 October 2022 / Accepted: 16 October 2022 / Published: 20 October 2022 (Open Access) Loss of Generator. on the system. Frequency Falls as. demand > generation. Stored energy delivered to grid as MW. The stored ener... https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1073/15/20/7767
· Grid Code Frequency Response Working Group System Inertia, Antony Johnson, System Technical Performance, September 2, 2010, National Grid (London, UK.)
https://www.nationalgrid.com/sites/default/files/documents/16890-Meeting%208%20-%20Inertia%20presentation.pdf
· California ISO (CAISO) Frequency Study, Nicholas W. Miller, Miaolei Shao, and Sundar Venkataraman, 09 November 2011, GE Energy, Schenectady, NY. https://www.caiso.com/Documents/Report-FrequencyResponseStudy.pdf
CGNP questions some of the key assumptions in CAISO's 2011 frequency study.
For further information, See
A2312014 CGNP Redacted Amended Testimony in Support of the Helms Uprate 02 27 25A23120
and
CGNP’s A2312014 Appendices dated 02 15 25 at
https://cgnp.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/A2312014-CGNPs-Appendices-02-15-25.pdf









There are actually four turbines, one very heavy generator rotor and one small exiter rotor connected to one shaft at DCPP.
The 3 low pressure steam turbines are approximately 100 tons each and the generator rotor is about 150 tons, so the mass moment of inertia can’t be the same as Helms, I’ve been to both plants, so I agree, there is no comparison.
DCPP’s 500 tons of spinning mass at 1800 rpm is absolutely the largest contributor to SGI in California, no doubt!